- Home
-
Biogas Projects
By Size By Gas Utilization By Application
- Biogas Plant Technology
- Service
- Blog
- Resources
- Company
- Contact
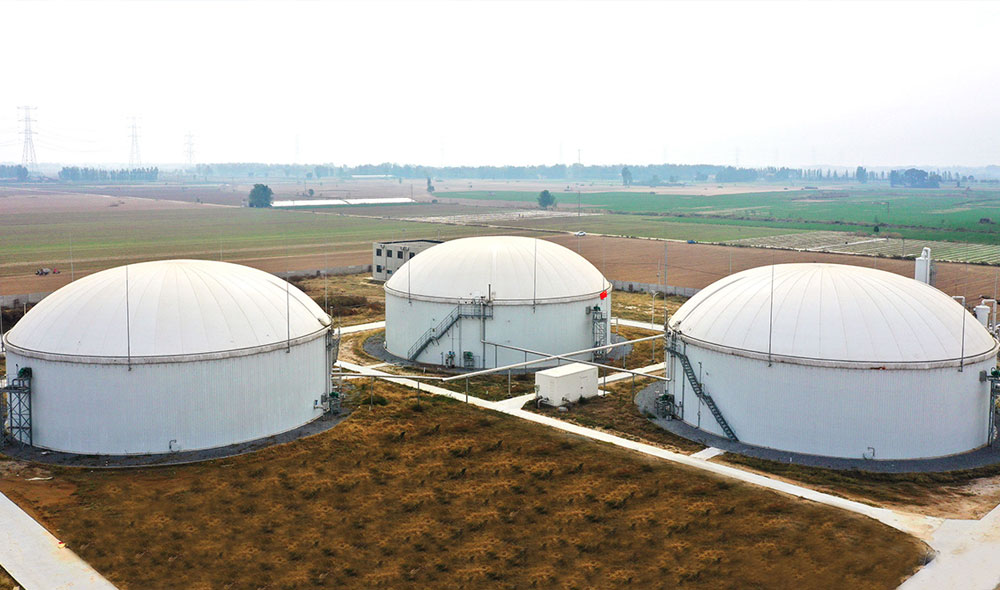
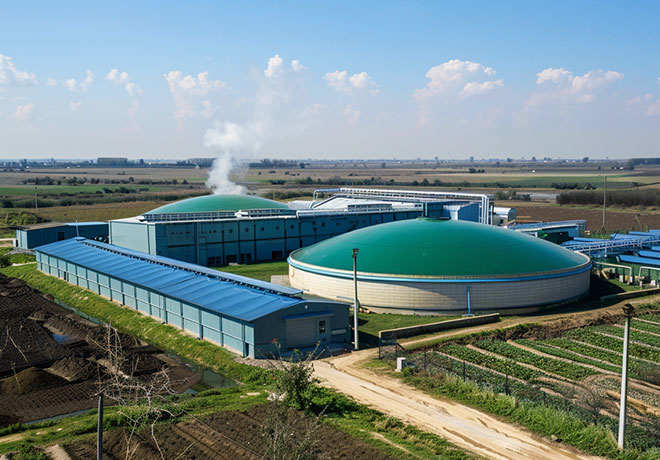






The biogas project utilizes a diverse array of organic materials, sourced from agricultural residues, animal manure, sewage wastewaters, integration crops, and the organic fraction of municipal waste collected from various sources. Agricultural residues encompass leftover materials from crop harvests such as corn stover, wheat straw, and sugarcane bagasse. Additionally, animal manure, often mixed with bedding materials like straw or sawdust, contributes to the feedstock. Sewage wastewaters provide another valuable input with the help of bio gas plant suppliers, alongside integration crops specifically cultivated for energy production. Furthermore, the organic fraction of municipal waste, gathered from households, institutions, and industries, enriches the feedstock blend, ensuring efficient biogas production.
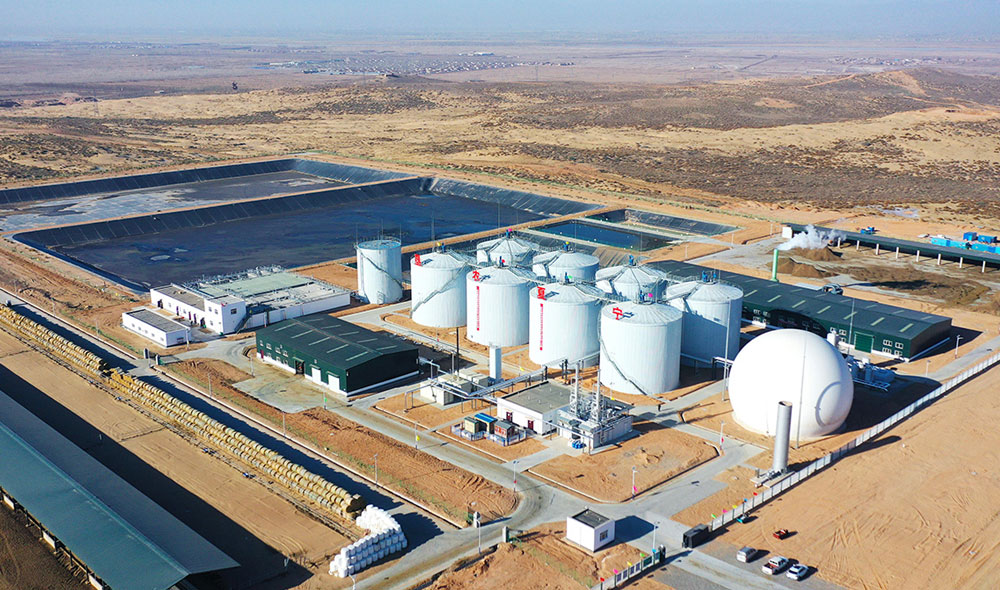
Large-scale biogas projects are technologies that utilize organic waste (such as agricultural waste, animal manure, industrial wastewater, municipal garbage, etc.) to produce biogas through anaerobic digestion.
Biogas is a renewable energy source, mainly composed of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be used for power generation, upgrading natural gas, heating, and more. The typical process flow of a large-scale biogas project is as follows:
Collection of raw materials: Collect agricultural waste, animal manure, industrial wastewater, municipal garbage, and other organic waste.
Pretreatment: Preliminary treatment of raw materials, such as removing large impurities and shredding, to facilitate subsequent anaerobic digestion.
Crushing: Further crush the raw materials to reduce particle size, increase surface area, and facilitate microbial contact and fermentation.
Parameter adjustment: Adjust parameters such as the temperature of the raw materials as needed to adapt to the growth of anaerobic microorganisms.
Feeding: Pump the pretreated raw materials into the digester.
Fermentation: In the digester, microorganisms decompose organic matter to produce biogas. This process usually takes a certain amount of time, with HRT for manure materials generally around 15 days and for straw materials around 25 days.
Mixing: To maintain a uniform mixture of microorganisms and raw materials inside the fermentation tank, the materials inside the tank need to be stirred to achieve a uniform mixture.
Parameter adjustment: Adjust parameters such as the temperature of the raw materials as needed to adapt to the growth of anaerobic microorganisms.
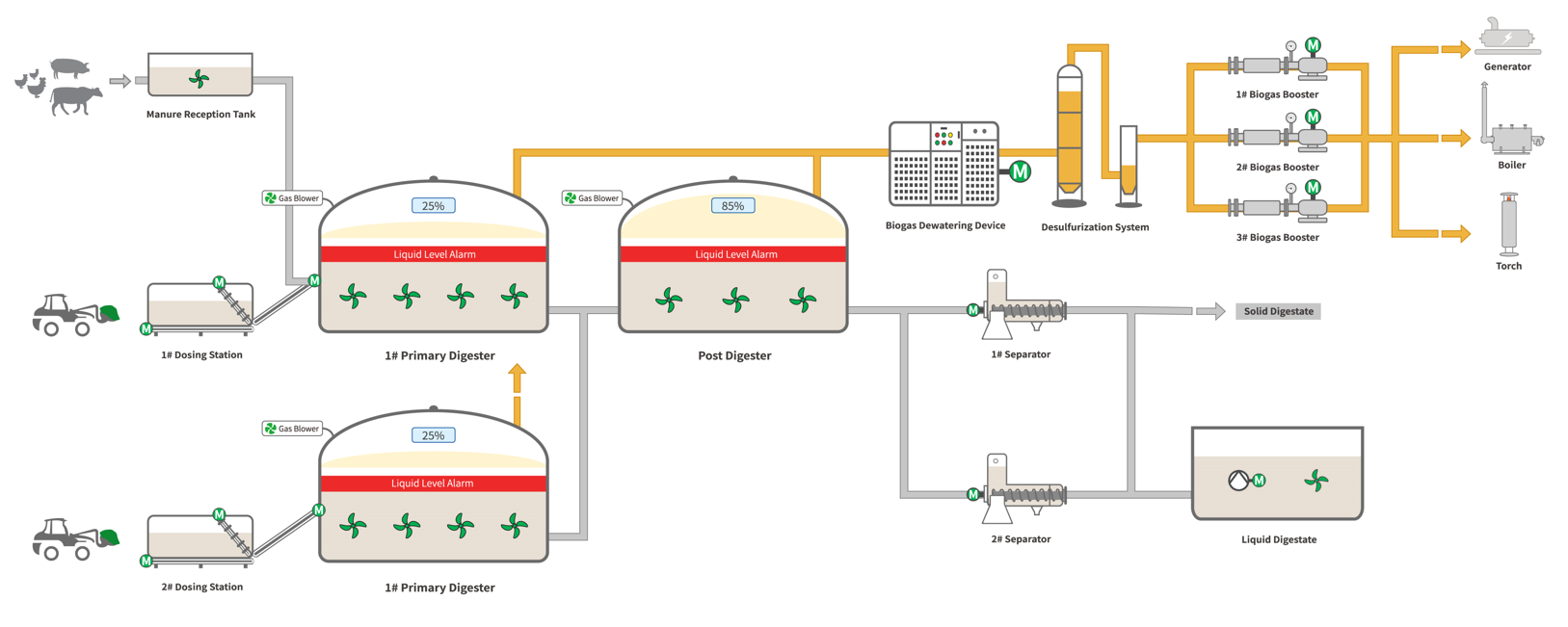
Collection: Biogas is released from the digester and collected in a gas holder through pipelines.
Storage: The collected biogas is stored in gas holder for subsequent use.
Desulfurization: Biogas contains impurities such as hydrogen sulfide, which need to be removed through a desulfurization device to prevent corrosion of equipment and the environment.
Dewatering: Remove moisture from biogas to increase its calorific value.
Power generation: Use biogas to drive gas turbine generator sets to produce electricity.
Heating: Biogas can be used in heating systems to provide thermal energy.
Upgrading: Biogas can be processed through an upgrading system to increase methane concentration as fuel, and can also be further compressed into CNG for use in vehicles, boilers, etc.
Chemical raw materials: Methane in biogas can be used as a chemical raw material for the production of plastics, synthetic rubber, and other products.
In the international community, there are no specific regulations for biogas projects, and the design of the overall biogas project should fully consider the feeding of raw materials, the smooth process of biogas production, purification and utilization.
Large biogas projects help fight global warming by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, providing renewable energy, managing waste effectively, supporting sustainable agriculture, enhancing energy security, and offering economic and environmental benefits.
Biogas plant can be handle plant straw(Corn/paddy/wheat),Napier grass,Bagasse,POME,Animal slurry and manures,Kitchen and food waste,Agriculture organic wastes,sludge,Dead or diseased animal body.Biogas plant suitable for animal farm manure and agriculture farm treatment solutions.
We expect that the daily output of biogas can be greater than 10,000 cubic meters, and only when a certain scale economy is achieved, the overall biogas project investment efficiency will be good.
Maintaining a large-scale biogas system requires regular inspections, proper feedstock management, digester cleaning, temperature control, and safety checks. It's also important to manage biogas storage and distribution, sludge, and to train staff. Preventive maintenance and compliance with regulations are crucial, as is monitoring and record-keeping to ensure the system operates efficiently and safely.